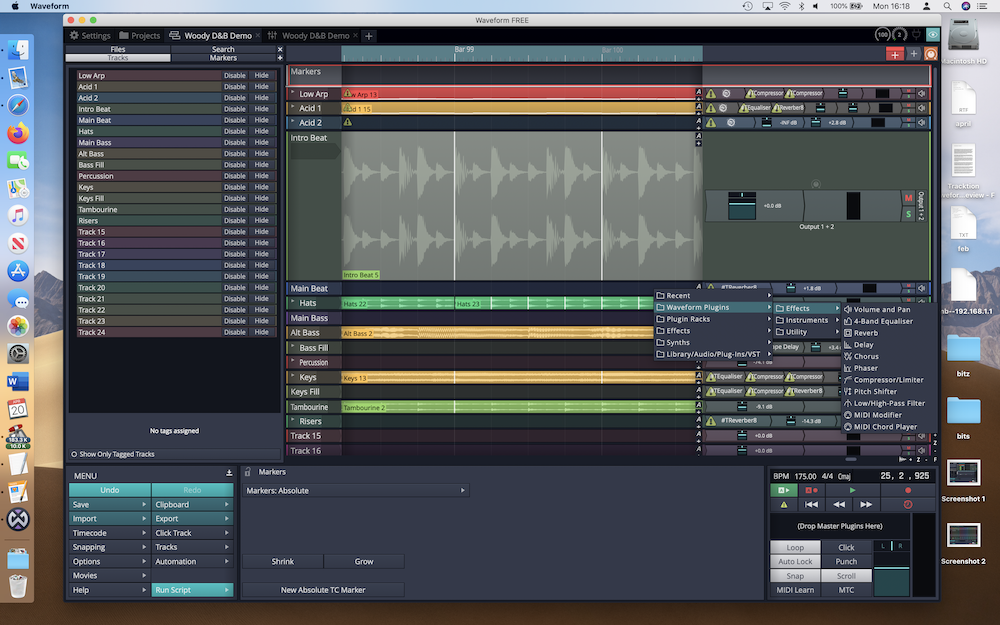
What is an Audio Waveform?
The waveform was a Force technique used by the Selkath adepts of the Order of Shasa. Inspired by the oceans of Manaan, waveform techniques allowed Order devotees to enhance telekinetic abilities by manipulating the natural wave patterns in nature and the particles of the surrounding environment. The waveform's intended user becomes another imperative in the waveform's design, according to Mr. Kroon: 'In the air, aircraft move a lot faster than vehicles on the ground. Some work well with fast moving aircraft, and some do not work so well.'.
As a matter of fact, a waveform is merely a graph that displays amplitude or level changes over time. Amplitude is measured in a bipolar manner, with positive and negative values; not to be confused with level, which can be the absolute value of amplitude changes or an average.
What makes this concept abstract is that waveforms typically contain tens of thousands of discrete changes within an unimaginably short period, crammed into a short block in a sequencer. As you probably already know, as you zoom in on a waveform, its contour becomes more and more visible.
Cyber-Ops is an online community in The Netherlands. We are a community of people who have different backgrounds, those who work active in the military, wish to work in the military, those who work, wish to work in the cybersecurity world of digital conflicts (a.k.a. Conquering cyberspace With the constant evolution of today's technology, information and communications can be optimized like never before. Responsible for a wide range of weaponry, training and intelligence efficiencies, Cyberspace Operations. The new Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate certification replaces the current CCNA Cyber Ops certification. Beginning May 29, 2020, Cisco will release an updated, consolidated exam, 200-201 CBROPS, that will replace the current 210-250 SECOPS. The Performing CyberOps Using Cisco Security Technologies v1.0 (CBRCOR 350-201) exam is a 120-minute exam that is associated with the Cisco CyberOps Professional Certification. This exam tests a candidate's knowledge of core cybersecurity operations including cybersecurity fundamentals, techniques, processes, and automation. Cyber ops. Cyber Ops is a story-based tactical hacking game, told from the point of view of a mission control supervisor, operating from the distance. You are the eye in the sky, the invisible hand, the cyber ghost, looking after your team over the net.
—–Zoom——>
PCM and NYQUIST FREQUENCY
A waveform is a digitized recreation of very dynamic voltage changes over time. Here is how they are typically generated….
The discrete changes in an input signal are rectified in an instant through a process called 'Pulse Code Modulation' (PCM). Simply put, PCM assigns a bit value to each sample at whatever sampling rate you're running. Furthermore, the higher the bit depth, the more values the computer has to choose from and the more accurate the rectification is. Sampling Rate for recording purposes is pretty standard – 44100 Hz, the Nyquist Frequency for audio. Here is why it is standard…
- The highest audible frequency for humans is 20,000 Hz.
- Every frequency has a positive half and a negative half (compression and rarefaction).
- So, as long as we sample (analyze and generate) rapidly enough to catch both the positive and negative portions of the highest (most rapidly oscillating) audible frequency – we can confidently rectify just about every audible frequency.
- This means at a sampling rate of 40000 Hz, we will catch both the positive and negative portions 20,000 Hz. However, since sine waves are infinitely smooth and gradual, just one sample of each portion will not produce a very accurate waveform at very high and very low frequencies – but this gets pretty close. This is why the extra 4100 Hz in Nyquist Frequency exists. It accounts for any aliasing that may occur when sampling very low and very high frequencies.
Of course at this point you may be asking yourself 'Why not just sample as frequently as possible? Why not just go to 50,000 Hz or 100,000 Hz?' The answer is negligence. We cannot hear the improvement past 44100 Hz. BUT THIS DOES NOT MEAN OTHER SAMPLE RATES ARE NOT USED. For example, when producing sound or music for film, the sample rate of the audio should match the video resolution rate – which is often over 90,000 Hz.
SYNTHETIC WAVEFORMS

Waveformer
Synthetic waveforms are MILES less complex than audio recorded from an acoustic or electrical source. This, frankly, is the beauty of them – they allow us tocreate sounds from scratch without getting ahead of ourselves. After all, every frequency part of a sound – harmonic or not – has the potential to send you down a path of unintentional, unfocused ideas that will do more harm than good in context. These are the four basic synthetic waveforms.
Sine
One harmonic, one frequency. So perfectly simple that it cannot technically exist acoustically or electrically. On the whole, even the purest sounding oscillators and self-resonating filters have a little bit of noise in their output. Y= Asinx describes it mathematically.
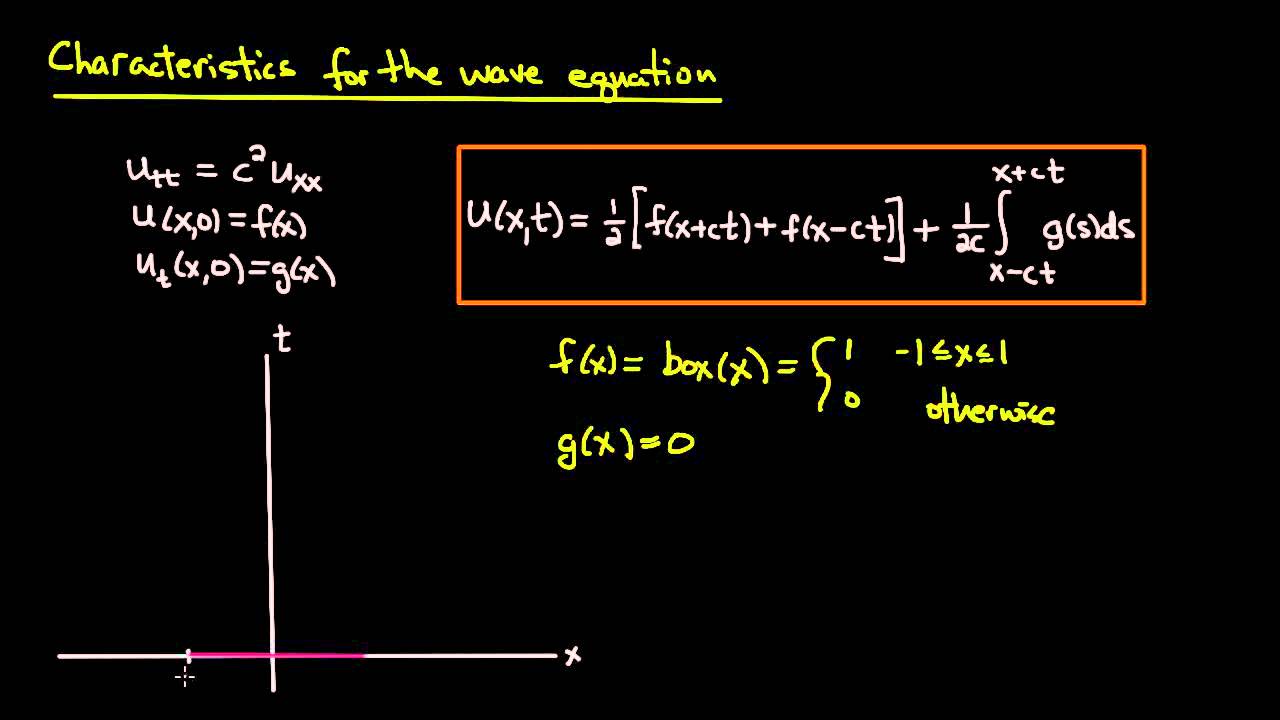
Square
Contains odd harmonics (odd whole number multiples of the fundamental). This means that if the fundamental frequency of a square wave is 200 Hz, it will also generate 600 Hz (3rd harmonic), 1000 Hz (5th harmonic), 1400 Hz (7th harmonic) and so on….
Waveform 11 Pro
Triangle
In short, Triangle is like a square wave in that it contains odd harmonics, except the harmonic content, is lower in amplitude than in a square wave. Meaning, the harmonics have less influence on the overall shape of the wave.
Sawtooth
Contains all harmonics. This means that this is the most complex of the four basic synthetic waveforms – but still nowhere close to as complex as real sound. In addition, ff the fundamental of a sawtooth is 100 Hz, that means it also contains 200 Hz, 300 Hz, 400 Hz ….etc. Each harmonic is a little lower in amplitude in comparison to the previous one.

Waveformer
Synthetic waveforms are MILES less complex than audio recorded from an acoustic or electrical source. This, frankly, is the beauty of them – they allow us tocreate sounds from scratch without getting ahead of ourselves. After all, every frequency part of a sound – harmonic or not – has the potential to send you down a path of unintentional, unfocused ideas that will do more harm than good in context. These are the four basic synthetic waveforms.
Sine
One harmonic, one frequency. So perfectly simple that it cannot technically exist acoustically or electrically. On the whole, even the purest sounding oscillators and self-resonating filters have a little bit of noise in their output. Y= Asinx describes it mathematically.
Square
Contains odd harmonics (odd whole number multiples of the fundamental). This means that if the fundamental frequency of a square wave is 200 Hz, it will also generate 600 Hz (3rd harmonic), 1000 Hz (5th harmonic), 1400 Hz (7th harmonic) and so on….
Waveform 11 Pro
Triangle
In short, Triangle is like a square wave in that it contains odd harmonics, except the harmonic content, is lower in amplitude than in a square wave. Meaning, the harmonics have less influence on the overall shape of the wave.
Sawtooth
Contains all harmonics. This means that this is the most complex of the four basic synthetic waveforms – but still nowhere close to as complex as real sound. In addition, ff the fundamental of a sawtooth is 100 Hz, that means it also contains 200 Hz, 300 Hz, 400 Hz ….etc. Each harmonic is a little lower in amplitude in comparison to the previous one.
To conclude, IT IS IMPORTANT TO REALIZE that triangle, square, and sawtooth waves ARE MADE UP OF SINE WAVES – AS IS EVERY SOUND IN THE UNIVERSE. In essence, one can synthesize a somewhat accurate square wave by adding odd multiples of the fundamental frequency to a sine wave. In the audio below, I have done just that! Listen to the sine wave gradually form into a square wave as I sweep in odd harmonics. The synthesized square wave plays in isolation at the end. I have isolated each partial on a different track and, in doing so, created a crude 'spectrum' analysis of the sound.
https://soundbridge.io/wp-content/uploads/2015/09/WF.-Sin-to-Sq.mp3When to Use Phase-Coded Waveforms
Situations in which you might use a phase-coded waveform insteadof another type of waveform include:
When a rectangular pulse cannot provide both of thesecharacteristics:
Short enough pulse for good range resolution
Enough energy in the signal to detect the reflectedecho at the receiver
When two or more radar systems are close to each otherand you want to reduce interference among them. Hollow knight nightmare king.
When digital processing suggests using a waveformwith a discrete set of phases. For example, a Barker-coded waveformis a bi-phase waveform.
Conversely, you might use another waveform instead of a phase-codedwaveform in the following situations:
Atom rpg: post-apocalyptic indie game. When you need to detect or track high-speed targets
Phase-coded waveforms tend to perform poorly when signals haveDoppler shifts.
When the hardware requirements for phase-coded waveformsare prohibitively expensive
